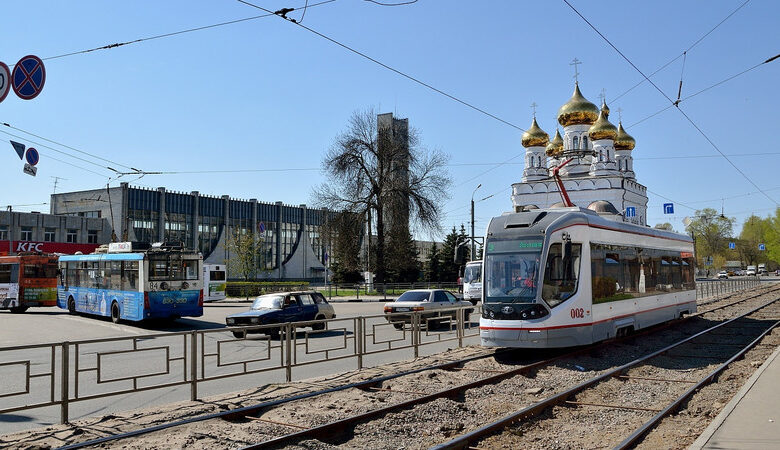
The suffix may not be indicated by letters. The suffix may not be indicated by letters. Morphemic analysis of the word suitable 1. A suffix is a morpheme that comes after the root and usually serves to
The suffix may not be indicated by letters. The suffix may not be indicated by letters Morphemic analysis of the word suitable
1. Suffix – this is a morpheme that comes after the root and usually serves to form new words, although it can also be used to form the form of one word.
For example: kind – kindness (suffix –from – derivational) kinder, kinder (suffix –her – formative, forms the form of the comparative degree of the adjective; suffix –eysh – formative, forms the form of the superlative degree of the adjective).
In some cases, the suffix -j- may not receive a special graphic designation in the word. Its presence can be indicated by vowels e, e, u, i in a position after a consonant or a dividing b, for example: Volga region [j]e [pΛvolzhj], Zaonezh [j]e [zΛn'ezhj].
2. Most suffixes are used to form new words.
Teach – teacher, teachers about, teacher's.
There are relatively few formative suffixes in Russian. The most important among them are the following:
suffixes of the comparative and superlative degrees of the adjective: -her (-ey), -e, -she, -eysh-, -aysh;
Faster, faster, more expensive, older, deepest, wisest.
verb past suffix -l;
Came and found out.
verb imperative suffix -i;
Take it, take it.
some suffixes of nouns as indicators of plural and singular;
Wed: citizen (unit) – citizens (pl.); friend (unit) – friends (plural; it is created not only due to the ending -i [a], but also due to the suffix -j- – [druz'j aʹ]); son (unit) – son i (plural; it is created not only due to the ending -i [a], but also due to the suffix -ovj – [sonΛv'j aʹ]); duckling ok (unit) – ducklings a (pl.).
some suffixes of nouns as indicators of oblique cases.
Wed: mother – (No) mater and , time – (No) times and.
The spelling of suffixes depends on the part-of-speech attribution of the word and therefore will be considered when characterizing the corresponding parts of speech.
1) In linguistics, there is no unity in determining the status of the indicator of the indefinite form of the verb (infinitive) – -t, -ti, -ch (run, carry, save ). Some researchers characterize these morphemes as an ending, others as a suffix. In this guide, we are looking at infinitive indicator (-th, -ty, -ch) like an ending (!).
2) In linguistics, there is no single point of view on participle affiliation (reading, reading, reading, reading ) and gerunds (reading, reading ). In some manuals, participles and gerunds are characterized as independent parts of speech (and in this case the corresponding suffixes will be word-building), in others – as special forms of the verb (and then the same suffixes will be form-building).In this manual, participles and participles are considered as independent parts of speech.
3. As roots and consoles, suffixes can change their appearance. At the same time, as in the roots, the alternations of consonants and vowels are observed here. In particular, “runaway vowels” are possible.
Cf.: Books -K -a -Book -Ek; slippery -k -y -slippery, funny -n -oh -funny, old -tier -old -ts -a, dishes -t -e -dishes.
Regularly regularly in the suffixes there are alternations of consonants and combinations of sounds (c /h, ov /y).
Cf.: Books -K -a -Book -Ych -k -A, Kom -Ok -Com -Och, Pir -I -Vo -Pir -Uj -I.
4. In general, when selecting suffixes and suffix complexes, it is necessary to focus on the words from which this word is formed. At the same time, it is convenient to use periphrase with such a single -rooted word.
-
Compare the morphemic composition of nouns: Sasha, cherry, pea.
In the word Sasha (Sash-A ) the root stands out Sash- (Sasha ) and suffix -enk (a ): «Sasha – diminutive to sash a ».
In the word cherry (cherries-ka ) the root stands out cherry- With a cursory vowel (cherry ) and suffix -to (a ): «Cherry – Little cherry I ».
In the word pea (pea ) the root stands out pea- With alternating consonants X /Sh (peas ) and two suffixes: suffix -in- (pea ): «Pea – a single component of peas ”; suffix -to (a ): «Pea – Little peas In ».
In the word dreamy (dreamy ) the root stands out Dream- (dream ) and three suffixes: the suffix of the verb -a- (dream ): «Dream – Draw a dream am ; suffix -The with the meaning of the figure (dreamer ): «Dreamer – The one who loves dream at ; The suffix of the adjective -n (th ): «Dreamy – such as a dreamer; The characteristic dreamer Yu ».
In the word conscious (conscious ) the root stands out know- (know ) with the prefix co- (Co-TO ), as well as one suffix -The (th ): «Conscious – one who is correctly Ayet , understands the surrounding reality. Suffix -The In this case, it does not stand out, since there is no noun in the Russian language Conscious .
The most typical errors when highlighting the suffixes are the following.
1) Carrying the end letters of the suffix to the end. This is especially common with suffixes: -enj (e ) – Vlad -Jenj -Ye, thj (e ) – Take-tej-e, -yj (e ) – Self-love-ij-e, -j (e ) – Happiness-j-th, -j (e ) – Jen-j-oh, -Azij (I ) – DELOG ACIJ-I, -IJ (I ) – ARM-IJ-I . In all these cases Ij or J. Relate to the suffix, and not to the end (!).
2) The attribution to the suffix of part of the root or part of the previous suffix (usually in the presence of the word of the same sounds and letters).
3) The indifference of individual suffixes and the amount of suffixes.
Cf.: Core- ose (from Kosn th , where Kosn – – root), ready -Do (from ready th , where ready – – root), literacy ose (cf.: letter –a → literal -N –th → literacy ose).
Russian language lesson in grade 3
Prepared by the teacher of MBOU secondary school No. 11 MBOU secondary school No. 11
Lebedintseva N.I.
Technological map of the study of the topic
Academic subject
Lesson of opening new knowledge
Technology for building a lesson
What is a suffix? How to find a suffix in the word?
Creating conditions for mastering students' knowledge about the suffix;
for the formation of UUD students (cognitive, regulatory, communicative); to form an understanding of the need for teaching.
Planned result
Subject skills
The composition of the word (morphemic)
own identification features of the same -root words;
find the ending, root, suffix in words with unambiguously distinguished morphemes;
highlight the zero ending;
To form words with the help of a suffix, to realize the meaning of new words.
recognize parts of speech on the basis of learned features
the formation of an internal position of the student at the level of a positive attitude to school, the study of the Russian language, understanding the need for learning;
Orientation on the development of cooperation skills with a teacher, adults, peers in the process of performing joint activities in the lesson.
accept and maintain a goal and educational task; In cooperation with the teacher, set new educational tasks;
take into account the rule (algorithm) in planning and monitoring the solution method;
perform actions according to the plan, as well as according to the instructions contained in the sources of information (in the tasks of the textbook, reference material of the textbook – in memos);
To evaluate your achievements, determine difficulties, realize the causes of success and failure and ways to overcome difficulties.
realize the cognitive task, solve it (under the guidance of a teacher or independently);
understand the information presented in the visual, graphic form; Put it into verbal shape.
Participate in dialogue, general conversation, joint activities (in groups), negotiate with partners about ways to solve the educational problem, come to a common solution.
Work in groups
Printing products:
Russian language. Grade 3. Textbook. for general education. institutions from adj. On the electron. media. In 2 hours. Part 1 / V.P. Kanakina, V.G. Goretsky. 2nd ed. – M. Education, 2017.
Technical learning tools:
Hard-sound manuals:
Presentation in Power Point
Teacher's activities
The activity of the student
Greet guests.
The long -awaited bell is given
The lesson begins!
Well, now check, my friend,
Are you ready to start a lesson?
Everything is in place
Everything is good,
Pen, book and notebooks?
Teachers welcome, check the readiness of their workplace, tune in to work.
Motivation for educational activities
– What topic do we study? Guests came to our lesson.
– Look at them, who can tell about them?
The guys talk about the root, ending, prefix. The last appears a suffix
Actualization of knowledge and trial educational action
– Formulate the topic of the lesson.
Executive 164 (p. 89 ) . Read the poem, find the same -rooted words and write them out.
The whole family goes for a walk
At night along the tracks
Hedgehog – father, hedgehog – mother
And the child is a hedgehog.
(S.Ya. Marshak )
-What word did the word Hedgehog and hedgehog formed? Highlight these parts. Where are they in front of the root or after the root?
They work in groups (3-4 people): write words, select the root, ending, suffix cannot be distinguished.
Students perform tasks, check the completed according to the standard
Identification of the place and cause of difficulty
Reveal the cause of difficulty.
– I still can’t highlight the suffix because …
Building a getting out of difficulty
Offers to formulate the tasks of the lesson.
Formulate the tasks of the lesson.
Implementation of the constructed project
Ex. 165 (p. 89).
Answer the questions:
What is a suffix?
Where is the suffix?
Why does it serve?
Students work with the textbook, a record is being recorded, answer questions,
Monitor the change in the lexical meaning of words.
Students answer questions, formulate the rule
They read the rule in the book on their own and determine what new learned about the suffix.
Primary consolidation with commenting in external speech
It offers to determine if all the objectives of the lesson have been achieved.
It offers to work in groups and make an algorithm for the suffix in the word.
Make an algorithm.
Choose _________________ words.
To find ________, ___________.
Part of the word that stands after the root and will be __________.
Students distinguish the suffix in words.
It is determined that one of the goals to learn to find in the word suffix.
Students work in groups, make up an algorithm.
Independent work with self -testing on the standard
Ex. 167 (p. 90).
They perform the task on their own and check during the commenting.
Inclusion in the knowledge system and repetition
Offers to fulfill orally UPR 166 p. 90
-Wall what residents of Tver are called? (Tverichi), suffix –ICH,
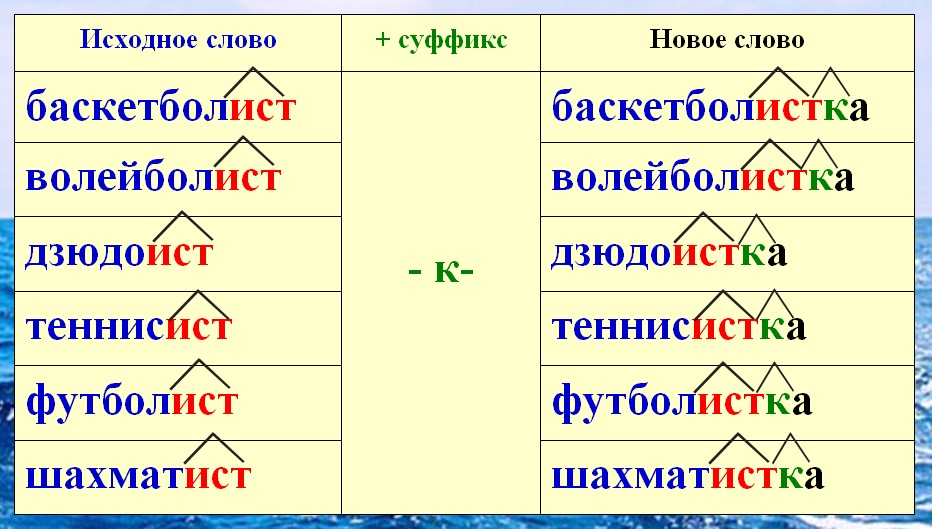
A game. It offers to form words (names of the inhabitants of the city) from the names of the cities of Moscow, Krasnodar, Anapa.
5*. Simpatient Sharanda.
My root is in price.
Find the prefix to me in the essay.
My suffix in a notebook you met,
All in the diary I am in the magazine.
They work frontally, form new single -stone words with the help of suitable suffixes.
Reflection of educational activities in the lesson
Offers to continue the phrase.
Today I found out …
It was interesting…
It was difficult…
I realized that …
Now I can…
I learned…
I could …
I was surprised …
I wanted…
Reflect their activities in the lesson.
Information about homework
B) offers to answer cunning questions:
– How to turn a big house into a small one?
– Is it possible to turn fish into a person?
– What should the tractor driver need to get a car?
Suitable analysis scheme for the composition:
Analysis of the word in composition.
The composition of the word suitable:
Connective vowel: is absent
PoCtfikc: is absent
Morphemes – parts of the word suitable
Detailed PAZBOP Suitable Po -Clot. COPN SLOVA, prefix, suffix and the end of the word. Moppem PAZBOP Suitable, hig CXMEMA and MOLOVA (MOPFEMS).
- Morphems Scheme: under/move/lining/IE
- Word structure by morphemes: prefix / root / suffix / ending
- Scheme (construction) words suitable in composition: prefix under + root move + suffix box + ending ie
- List of morphemes in the word suitable:
- under – prefix
- move – root
- box – suffix
- ee – ending
- prefix: under – 1
- root: move – 1
- connecting vowel: is absent – 0
- cyffix: crate – 1
- postfix: is absent – 0
- end: ie – 1
Total morphemes in the word: 4.
Word-building analysis of the word suitable
- Base word: suitable ;
- Derivational affixes: prefix under , suffix crate , postfix is absent ;
- Word formation: ○ prefix-suffix or prefix-suffix ;
- Way of education: derivative, as it is formed in 1 (one) way .
See also other dictionaries:
Decline the word suitable for cases in the singular and plural. Declension of words suitable for cases
Full morphological analysis of the word suitable: Part of speech, initial form, morphological features and word forms. The direction of the science of language, where the word is studied. Morphological analysis suitable
The stress in the word is suitable: which syllable is stressed and how. The word suitable is correctly spelled as. The stress on the word suitable
Anagrams (make an anagram) to the word suitable, by mixing letters. Anagrams for suitable
Morphemic analysis of the word suitable
Morphemic parsing of a word is usually called the parsing of a word by composition – this is the search and analysis of morphemes (parts of a word) included in a given word.
Morphemic analysis of the word suitable is done very simply. To do this, it is enough to follow all the rules and the order of parsing.
Let's do the morpheme parsing correctly, and for this we just go through 5 steps:
- determining the part of speech of a word is the first step;
- the second – we highlight the ending: for changeable words we conjugate or decline, for unchangeable words (gerunds, adverbs, some nouns and adjectives, service parts of speech) – there are no endings;
- Next, look for the base. This is the easiest part, because to determine the base, you just need to cut off the ending. This will be the basis of the word;
- The next step is to search for the root of the word. We select related words for suitable ones (they are also called single-root), then the root of the word will be obvious;
- We find the remaining morphemes by selecting other words that are formed in the same way.
As you can see, morphemic parsing is done simply. Now let's define the main morphemes of the word and analyze it.
* Morphemic word analysis (word analysis by composition) – search for the root, prefix, suffix, ending and stem of the word The parsing of the word by composition on the site is made according to the dictionary of morphemic parsing.
After vowels and after b, b, the letters E, E, Yu, I denote two sounds, one of which (or is often indicated). It is this sound that can be a suffix or part of a suffix.This proves the correctness of the selection of morpheme. You can check the correctness of analysis in a word -formation dictionary. Forms verbs with a return meaning.
Watch what is the “main suffixes of the Russian language” in other dictionaries:
In artistic works, suffixes can give words the desired emotional coloring: diminutive, affectionate, exaggerating. With the help of such words, the author (hero, narrator) expresses various shades of feelings: the suffix identifies and shows the speaker's attitude to the subject, quality, and attribute. Suffix – this term has other meanings, see the suffix (meanings). Borrowed words in the Russian language – borrowing foreign words one of the ways of developing a modern language. The language always quickly and flexibly reacts to the needs of society.
Moreover, in the vast majority of training options prepared by FIPI, in tasks, mainly verbs in the uncertain form, communion, participles, adjectives are really found. Can there be questions regarding the spelling of the suffixes of nouns? Verbs-exclusion to complete this task are not of interest: after all, you need to find out the letter not at the end, but in the suffix. You need to do others: learn to accurately determine from which verb the participles and participles are formed. What suffixes are these and how to write them, you have to figure it out.

The suffix -Ad- forms nouns with the meaning of a woman or wife: Popa. With the help of the same suffix, words can be formed from adjectives: Strings. Affixal morphous morphs, protruding only between two simple bases in a complex basis, are called interfixal (connecting).
Word -formation
Could you explain to me: how to determine whether one suffix is in a word or several? Arrived. It turns out that about each word you need to separately find out in the dictionary, for example, the suffix there is a good and suffixes -ov- and -nik-. And so with other words. But here it is necessary to understand the principles of word formation. And why is the topic in grammar, and not in word formation, by the way? In general, there is a morpheme …
Form -forming suffixes in the Russian language are relatively few. Some researchers characterize these morphemes as an ending, others as a suffix. The suffix -in this case does not stand out, since in the Russian language there is no noun conscious. 5. The suffixes occupy the position after the root before the end (if it is available in the word).
Suppose that it is necessary to determine the morphemic composition of the word run. At first glance, it consists of a root and zero ending. This suffix is zero: runager, blue, quiet than Ø (in addition, it should be noted along the way, they also have a zero ending). 1 In this case, we are talking only about the suffix way of forming words and its variety – zero suffix. The word-forming and morphous dictionary of the Russian language Galiullin K.R.(The word -formation nests and the division of the word into morphemes are presented). In what words in the modern Russian language prefixes are not distinguished?
For example: shift, study, years old, caring liv. 3) —The – serves for the formation of swallowed them. noun. Some suffixes serve not only to create new words, but also necessary for their stylistic coloring.
This is easy to do if you choose the same root words. You can take the word tradition, which is motivating for this adjective. In the word “tradition”, the ending is, to be more precise, -ja, the rest is the root, which means that in the sophisticated word you need to highlight the root of “tradition”. The suffix is such a part of the word with which you can replenish the vocabulary of the language and expand its diversity. The analysis of the word in parts is studied by morphemic. On dictations, presentations and exams, quite often there is a task for analyzing the word. There is nothing complicated in the analysis of the word, the main thing is to understand the basic rules of analysis and learn morphemes.







