Pulmonary tuberculosis – a description of the disease, classification, symptoms in adults and children, the causes of the disease, diagnostic methods and methods of treatment of the disease, a list of recommended analyzes and research, which doctor to contact, complications and prevention
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Information from this section cannot be used for self -diagnosis and self -medication. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic examinations should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and proper prescription of treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Lung tuberculosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
Definition
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease transmitted by airborne droplets. Its pathogen is a bacterium Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Everyone can become infected, but children are especially susceptible to tuberculosis due to insufficiently formed immunity.
The disease is curable, but treatment takes a long time. Early diagnosis of tuberculosis is of great importance – the sooner it is detected, the less complications will cause.
The causes of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is transmitted by airborne and airborne droplets. Mycobacteria are in the smallest drops, which the patient with tuberculosis distinguishes during conversation, coughing, sneezing, etc.
The number of people infected with tuberculosis bacteria is approximately 25-30%. But only every tenth of them gets sick.
Not every patient with tuberculosis is distinguished by mycobacteria, but only the one who has the collapse of the lung tissue and bacterial excretion (in colloquial – an open form of tuberculosis). You can get a dose of mycobacteria without even contacting a sick person directly, since they are able to settle on particles of dust and remain on it under favorable conditions for up to 18 days.
Children are extremely susceptible to infections, and the lack of vaccinations leads to the fact that, having met a tuberculosis stick, the body does not recognize it as an alien agent and does not secrete antibodies to combat infection, but instead gives bacteria the ability to freely penetrate the lungs.
Among the adult population, the risk group on tuberculosis infection includes:
- elderly people,
- Persons suffering from chronic diseases (such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases),
- People with oncological diseases,
- People taking immunosuppressive drugs,
- Patients who have undergone heavy operations,
- Smokers.
- Primary tuberculosis complex. It occurs with primary infection with tuberculosis and occurs, as a rule, among children. It proceeds without pronounced symptoms, radiologically resembles pneumonia, so the diagnosis is difficult, not contagious.In most cases, a small focus is closed with a capsule, and the disease does not develop further.
- Tuberculosis of intra -breeding lymph nodes. It is characterized by the spread of tuberculosis foci in both lungs and defeat of the lymph nodes.
- Disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis. Tiny inflammatory tubercles are formed over the entire surface of the lungs. It can be sharp or chronic, it proceeds hard (with fever, intoxication) and wave -like.
- Focal pulmonary tuberculosis. In the lung, it forms from one to several inflammatory foci of not more than 1 cm in diameter. It can flow asymptomatic or with low temperature, malaise.
- Infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis. It is one of the complications of focal tuberculosis. It proceeds hard, with a long fever, weight loss, cough, hemoptysis can be observed.
- Caseous pneumonia. The severe form of pulmonary tuberculosis develops acutely, with severe intoxication, fever. It is characterized by massive inflammation and then the decay of the lung tissue with the formation of cavities in the lung. Most often occurs in patients with weakened immunity.
- Lung tuberculoma. In the lung tissues, an encapsulated focus of more than 1 cm in diameter is formed, inside which the lung tissue breaks in.
- Cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis. The severe form of tuberculosis, in which the destruction of the lung tissue occurs and large cavities (cavities) are formed in the lung. It arises as a complication of other forms of tuberculosis.
- Fibrous-cave-like pulmonary tuberculosis. It is the final stage of cavernous tuberculosis, when the cavity in the lung is finally formed.
- Cirrotic pulmonary tuberculosis. The last stage of pulmonary tuberculosis is characterized by the replacement of pulmonary tissue on the cicatricial. It occurs in 0.1-8% of cases, mainly in absurd or incorrectly treated patients. The formation of this form requires the years of the disease.
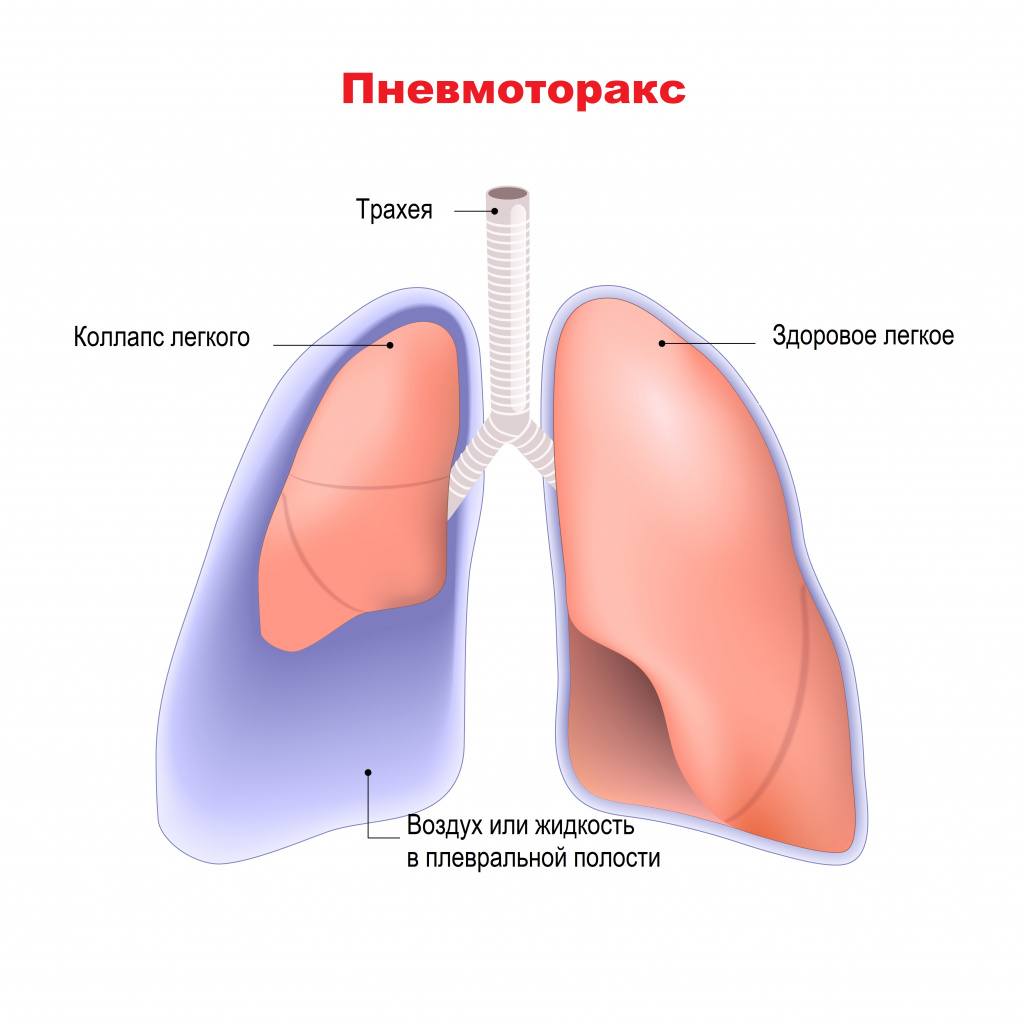
- Tuberculosis pleurisy. The inflammatory process affects the lung shell – pleura. It can develop as a complication of pulmonary tuberculosis or as an independent disease, especially in young people.
- Tuberculosis of bronchi, trachea, upper respiratory tract.
- Respiratory tuberculosis combined with professional dust diseases.
- with the release of mycobacterium tuberculosis (MBT+);
- Without isolation of mycobacterium tuberculosis (MBT -).
- Severe weakness, fatigue, chronic fatigue.
- Insomnia, nightmares.
- Reduced appetite and loss of body weight.
- Night sweating (it can be so strong that the patient has to change bedding).
- An increase in body temperature, mainly to subfebrile values, that is, not higher than 37.5 ° C. The temperature is kept constantly and is accompanied by chills.
- Cough. First, patients are worried about dry cough, but sputum appears as the disease progresses.
- Hemoptysis. It is typical for the later stages of tuberculosis.
- Pain in the chest. The pain that occurs when coughing indicates the involvement of the pleura in the pathological process.
- Strong shortness of breath.
-
Clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula (in order to identify an inflammatory process).
Synonyms: Complete blood count, KLA. Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study Clinical blood test: general analysis, leukocyte formula, ESR See also: General analysis – see test No. 5, Leukocyte.
Synonyms: Total serum protein; Total whey protein. Total Protein; Serum Total Protein; Total Serum Protein; TProt; TR. Brief description of the analyte Total protein Blood serum (blood plasma devoid of fibrinogen) contains many proteins that perform a variety of functions.
The test is intended for screening assessment of the composition and quantitative ratio of blood serum protein fractions by electrophoresis. Synonyms: Serum protein electrophoresis. SPEP. Brief description of protein fractions of blood serum Total protein of blood serum consists of a mixture of proteins with ra.
C-reactive protein is an acute phase protein that is a sensitive indicator of tissue damage during inflammation, necrosis, and trauma. Synonyms: Blood test for CRP; Serum C-reactive protein. C-reactive Protein (CRP), quantitative; C-reactive protein test; CRP test. Brief description of def.
Alanine aminotransferase is an intracellular enzyme involved in the metabolism of amino acids. The test is used in the diagnosis of lesions of the liver, cardiac and skeletal muscles. Synonyms: Glutamate pyruvate transaminase; Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase; SGPT. Alanine aminotransferase; S.
Synonyms: Glutamine-oxaloacetic transaminase; Serum glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (SGOT); L-aspartate 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase; GSHCHT. Aspartate aminotransferase; Serum Glutamicoxaloacetic Transaminase; SGOT; Got. Brief description of the analyte AST.
Synonyms: Blood test for LDH; lactate dehydrogenase; L-lactate; NAD + oxidoreductase; Lactic acid dehydrogenase. Lactate dehydrogenase Total; lactic dehydrogenase; LDH; L.D. Brief description of the analyte Lactate dehydrogenase LDH – cytoplasmic.
Synonyms: Blood test for creatinine; Serum creatinine; Serum creatinine, GFR estimate. Creat; Cre; Blood Creatinine; Serum Creatinine; Serum Creat. Brief description of the analyte Creatinine Creatinine is a low molecular weight nitrogen-containing substance, a metabolic product of crea.
Synonyms: Blood test for electrolytes; electrolytes in blood serum. Electrolyte Panel; Serum electrolyte test; Sodium, Potassium, Chloride; Na/K/Cl. Brief characteristics of analytes (Potassium, Sodium, Chlorine) Potassium (K+) Main intracellular cation. Cal.
Total calcium is the main component of bone tissue and the most important biogenic element that has important structural, metabolic and regulatory functions in the body. Synonyms: Blood test for total calcium; Total calcium in serum. Total blood calcium; total calcium; Bl.
Determination of DNA of causative agents of tuberculosis: complex of mycobacteria: M.Hemoptysis. It is typical for the later stages of tuberculosis.
Pain in the chest. The pain that occurs when coughing indicates the involvement of the pleura in the pathological process.
Strong shortness of breath.
Clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula (in order to identify an inflammatory process).
Synonyms: Complete blood count, KLA. Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study Clinical blood test: general analysis, leukocyte formula, ESR See also: General analysis – see test No. 5, Leukocyte.
Synonyms: Total serum protein; Total whey protein. Total Protein; Serum Total Protein; Total Serum Protein; TProt; TR. Brief description of the analyte Total protein Blood serum (blood plasma devoid of fibrinogen) contains many proteins that perform a variety of functions.
The test is intended for screening assessment of the composition and quantitative ratio of blood serum protein fractions by electrophoresis. Synonyms: Serum protein electrophoresis. SPEP. Brief description of protein fractions of blood serum Total protein of blood serum consists of a mixture of proteins with ra.
C-reactive protein is an acute phase protein that is a sensitive indicator of tissue damage during inflammation, necrosis, and trauma. Synonyms: Blood test for CRP; Serum C-reactive protein. C-reactive Protein (CRP), quantitative; C-reactive protein test; CRP test. Brief description of def.
Alanine aminotransferase is an intracellular enzyme involved in the metabolism of amino acids. The test is used in the diagnosis of lesions of the liver, cardiac and skeletal muscles. Synonyms: Glutamate pyruvate transaminase; Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase; SGPT. Alanine aminotransferase; S.
Synonyms: Glutamine-oxaloacetic transaminase; Serum glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (SGOT); L-aspartate 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase; GSHCHT. Aspartate aminotransferase; Serum Glutamicoxaloacetic Transaminase; SGOT; Got. Brief description of the analyte AST.
Synonyms: Blood test for LDH; lactate dehydrogenase; L-lactate; NAD + oxidoreductase; Lactic acid dehydrogenase. Lactate dehydrogenase Total; lactic dehydrogenase; LDH; L.D. Brief description of the analyte Lactate dehydrogenase LDH – cytoplasmic.
Synonyms: Blood test for creatinine; Serum creatinine; Serum creatinine, GFR estimate. Creat; Cre; Blood Creatinine; Serum Creatinine; Serum Creat. Brief description of the analyte Creatinine Creatinine is a low molecular weight nitrogen-containing substance, a metabolic product of crea.
Synonyms: Blood test for electrolytes; electrolytes in blood serum. Electrolyte Panel; Serum electrolyte test; Sodium, Potassium, Chloride; Na/K/Cl. Brief characteristics of analytes (Potassium, Sodium, Chlorine) Potassium (K+) Main intracellular cation. Cal.
Total calcium is the main component of bone tissue and the most important biogenic element that has important structural, metabolic and regulatory functions in the body. Synonyms: Blood test for total calcium; Total calcium in serum. Total blood calcium; total calcium; Bl.
Determination of DNA of causative agents of tuberculosis: complex of mycobacteria: M.Tuberculosis, M. Bovis, M. Bovis BCG, M. Microti, M. Africanum in sputum, flushing with bronchi, lavaid fluid using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with detection in “Real Time. Tuberculosis (from lat. Tubercul.
X -ray examination of the structure of the lungs in order to diagnose various pathologies.
A study that allows obtaining data on the state of the organs of the chest and mediastinum.
Diagnostic test with an intradermal sample for all age groups in order to diagnose tuberculosis infection.
A blood test permissible as an alternative to the skin test (mantle test) for the detection of tuberculosis infection. Tuberculosis is an infectious chronic disease caused by mycobacteria of tuberculosis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Comples). Active Tuberculosis Developed.
Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
- The success of treatment largely depends on the early diagnosis of the disease. Tuberculosis therapy is long and ranging from 4 months to several years.
- Self -termination of medication, passing or reducing dosage can cause resistance, that is, the stability of mycobacteria to antibiotics.
- During treatment, it is necessary to abandon smoking and drinking alcohol.
Tuberculosis therapy involves a combination of several antibacterial drugs. Basically, all drugs are taken in a tablet form, however, at the beginning of the disease or in severe course, their intravenous administration is required.





